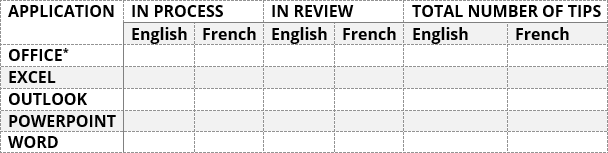
Many documents present some data in the form of figures or tables. Creating tables is often more efficient than describing the data in the paragraph text, especially when the data is numerical or large. The tabular data presentation makes it easier to read and understand.
A table is a collection of information or data, usually represented by horizontal rows and vertical columns. Each column and each row can have a header. Some tables have only column headings or only row headings. The box at the junction of each column and row is a cell that contains data such as text, numeric information, or images. Some cells can be merged or split (see more about formatting tables). E.g.:

Microsoft Word has many features that make working with tables simple and convenient.
There are several ways how to insert or create a table:
To create a blank table in a Word document, do the following:
1. Place your cursor where you want to insert the table.
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table button:
3. Do one of the following:
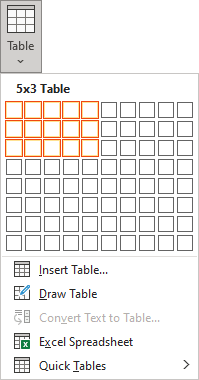
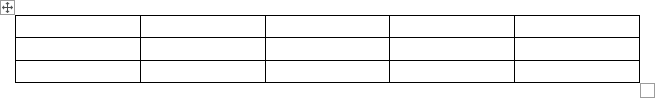
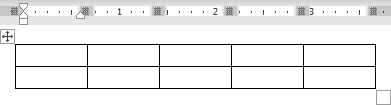
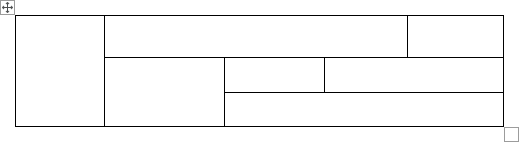
Click on a cell in the grid with the expected number of rows and columns (or press Enter) to insert an empty table to fit the width of the text (paragraph). The table has the specified number of single-line text rows in the current paragraph and equal-width columns. E.g., the table of 3 rows and 5 columns:
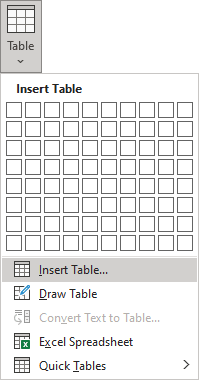
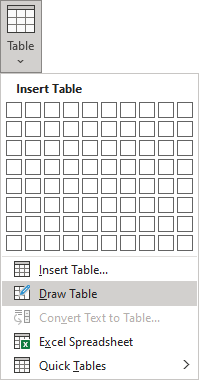
After clicking that option, the cursor changes to the pencil that allows drawing cells directly in the Word document to create a table:
To create a table using predefined Word templates of tables and calendars, do the following:
1. Place your cursor where you want to insert the table.
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table dropdown list, then select Quick Tables list:
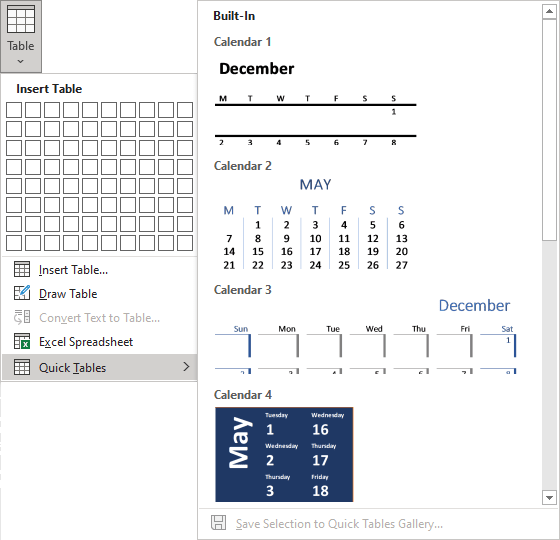
3. From the Quick Tables gallery, select the template you prefer.
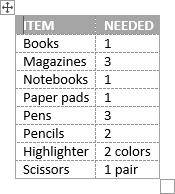
To create a table from the existing data in a document data (either as regular text or as a tabbed list), do the following:
1. Select the document data you want to shape into a new table.
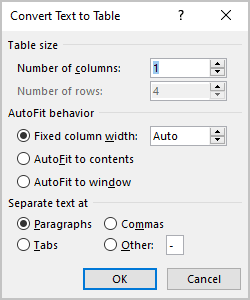
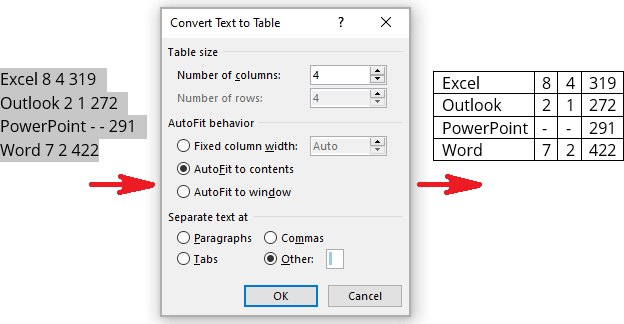
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table dropdown list, then select Convert Text to Table. :

3. In the Convert Text to Table dialog box:
Note: It is possible to insert a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet in a document. To do so, on the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table dropdown list, then select Excel Spreadsheet:
Word opens the Excel spreadsheet where you can enter the data. You can use Excel features such as functions and formulas to create or manipulate the data. Note that it is not a Word table.
To add a row and a column to a table, do the following:
1. Position the cursor:
2. Do one of the following:
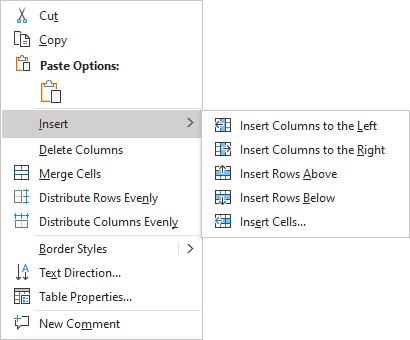
Notes:
 and
and 
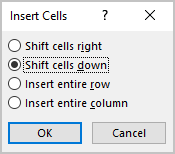
To delete a table element, do the following:
2. Do one of the following:
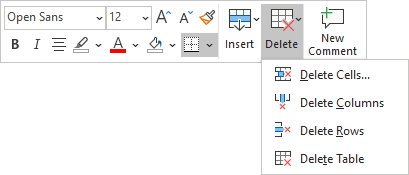
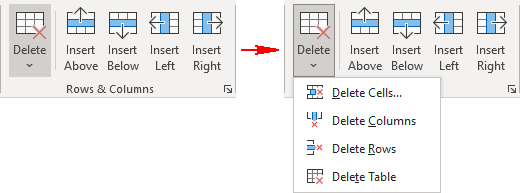
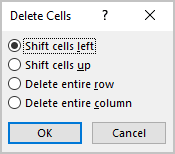
3. Select one of the proposed options:
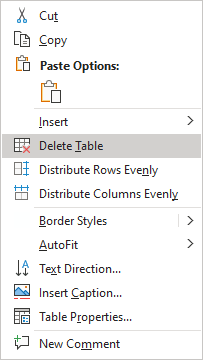
Note: You can select the element you want to delete, right-click on the selection and select the appropriate item in the popup menu. For example, if the entire table is selected or the column is selected:
 and
and 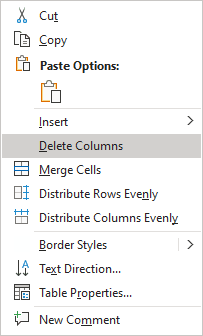
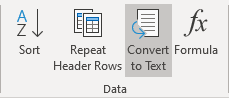
To convert a table into text in Word, follow the next steps:
1. Click anywhere in the table.
2. On the Layout tab, in the Format group, click the Convert to Text button:
3. In the Convert Table to Text dialog box, select the charter to separate cells data in the text:
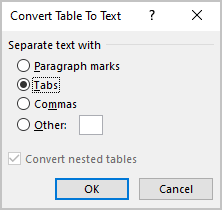
4. Click OK.
See also this tip in French: .
Today, 30% of our visitors use Ad-Block to block ads.We understand your pain with ads, but without ads, we won't be able to provide you with free content soon. If you need our content for work or study, please support our efforts and disable AdBlock for our site. As you will see, we have a lot of helpful information to share.

Many documents present some data in the form of figures or tables. Creating tables is often more efficient than describing the data in the paragraph text, especially when the data is numerical or large. The tabular data presentation makes it easier to read and understand.

After creating a table and filling it, the main task is to format the data and the table itself. The data in a table is formatted like any other text in Word by changing the font, aligning the text, etc.
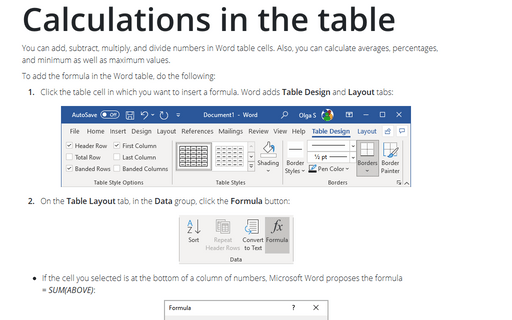
You can add, subtract, multiply, and divide numbers in Word table cells. Also, you can calculate averages, percentages, and minimum as well as maximum values.